Chromosomal Abnormalities in Cancer
Identifying Structural Aberrations
Genomic instability and chromosomal abnormalities are common features of cancer. Understanding these structural aberrations can provide insight into cancer etiology. Chromosomal abnormalities in cancer include gene fusions, chromosome rearrangements, and copy number variants (CNVs).
Sequencing- and microarray-based technologies offer complementary approaches for identifying chromosomal abnormalities in cancer.
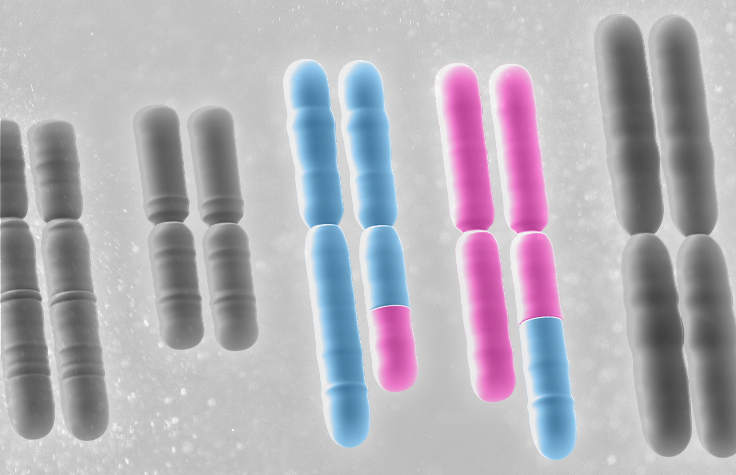
Analyzing Gene Fusions With RNA Sequencing
Gene fusions resulting from chromosome translocations are a common chromosomal abnormality in cancer, often driving tumorigenesis. Paired-end RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) enables researchers to identify non-contiguous sequences accurately by sequencing both ends of an insert.
Learn More About RNA-SeqDetecting Structural Variants With Mate Pair Sequencing
Mate pair sequencing is designed to detect structural variants. It provides sequence-specific information about each end of large DNA fragments for a comprehensive assessment of structural variants and chromosomal breakpoints and rapid identification of chromosomal abnormalities in cancer.
Learn More About Mate Pair SequencingIdentifying Copy Number Variants With Arrays
Microarrays are ideal for detecting CNVs, copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity, low-level mosaicism, and heterogeneity in cancer samples. Thousands of cytogenetically relevant genes are assessed in parallel to provide comprehensive coverage of chromosomal abnormalities in cancer.
Learn More About ArraysOur Products
Infinium CytoSNP-850K BeadChip Array
- Comprehensive coverage of cytogenetically relevant genes
- Expert-defined content1,2
- High detection sensitivity
iScan System
- Cutting-edge array scanner
- High sample throughput
- Industry-leading data quality
- Flexibility for multiple applications
TruSeq RNA Access Library Prep Kit
- Affordable solution for sequencing RNA from FFPE tissue
- Reduced sample input requirements while maintaining high sensitivity
Learn More

Array + NGS Chromosomal Studies
Lab analyzes chromosomal abnormalities and disease connection.

Cytogenetics Expert Interview
Dr. Trilochan Sahoo discusses microarray-based cytogenetic testing to detect chromosomal abnormalities in cancer.
Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on cancer genomics?
Sign Up
Cancer Research Review
An overview of recent cancer research publications featuring Illumina technology.
Cancer and Immune System Research Review
An overview of recent research publications exploring the interaction between tumor cells and the immune system.

Chromosomal Genetics Studies with Arrays and NGS
Laboratory adopts the newest technologies to analyze chromosomal abnormalities and their connection to disease.
References
- International Collaboration for Clinical Genomics (www.iccg.org)
- Cancer Cytogenomics Microarray Consortium (www.cancergenomics.org)